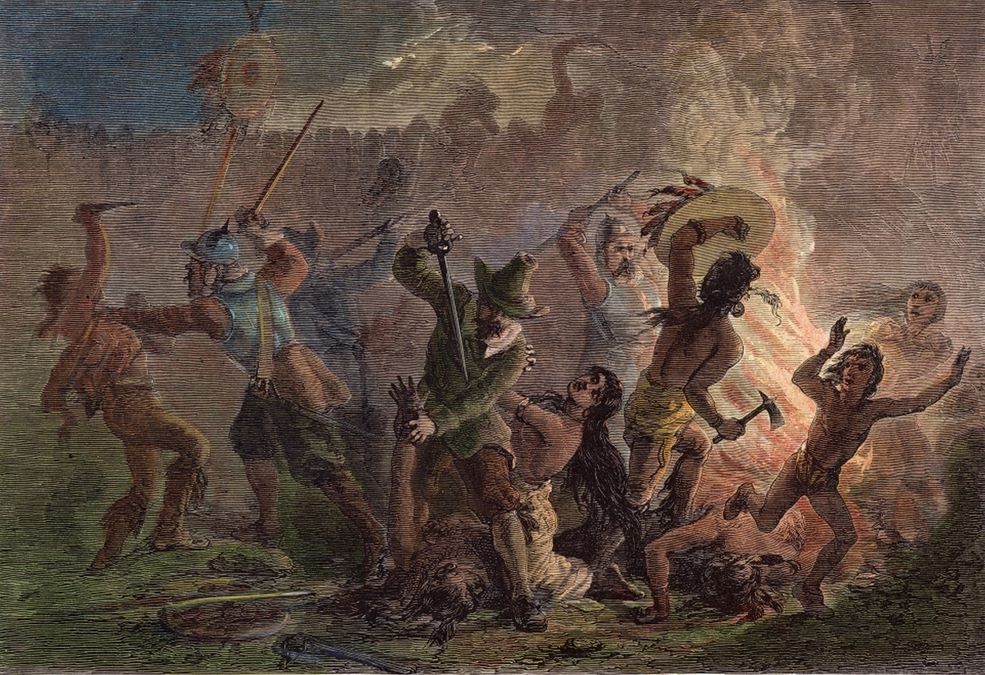The Pequot War was a significant conflict in early American history, taking place from 1636 to 1638 between the Pequot tribe and English settlers. This war marked one of the first major clashes between Native Americans and European colonists in New England. It resulted in devastating consequences for the Pequot people and set a precedent for future interactions between Native American tribes and European settlers. Understanding the Pequot War provides insight into the early colonial dynamics and the harsh realities faced by indigenous populations during European expansion.
The Pequot Tribe
The Pequot tribe, whose name means “destroyers” or “the men of the swamp,” inhabited the southeastern region of present-day Connecticut. They were a powerful and influential group, controlling trade and maintaining alliances with other tribes. The Pequot were known for their strong leadership and strategic prowess, which allowed them to dominate the area. Their society was complex, with well-established social structures and a deep spiritual connection to their land.

The arrival of European settlers in the early 17th century disrupted the balance of power in the region. The Pequot initially attempted to maintain peaceful relations and trade with the English, Dutch, and other European settlers. However, increasing competition over resources and territorial disputes eventually led to tensions. The Pequot’s strategic location and control over trade routes made them both valuable allies and formidable opponents to the colonists.
The Pequot War
The Pequot War erupted in 1636, primarily due to escalating tensions and competition for control over trade and territory. The conflict began with a series of violent encounters, including the murder of an English trader, which the colonists attributed to the Pequot. In retaliation, the English launched a series of attacks against Pequot villages, leading to a full-scale war.
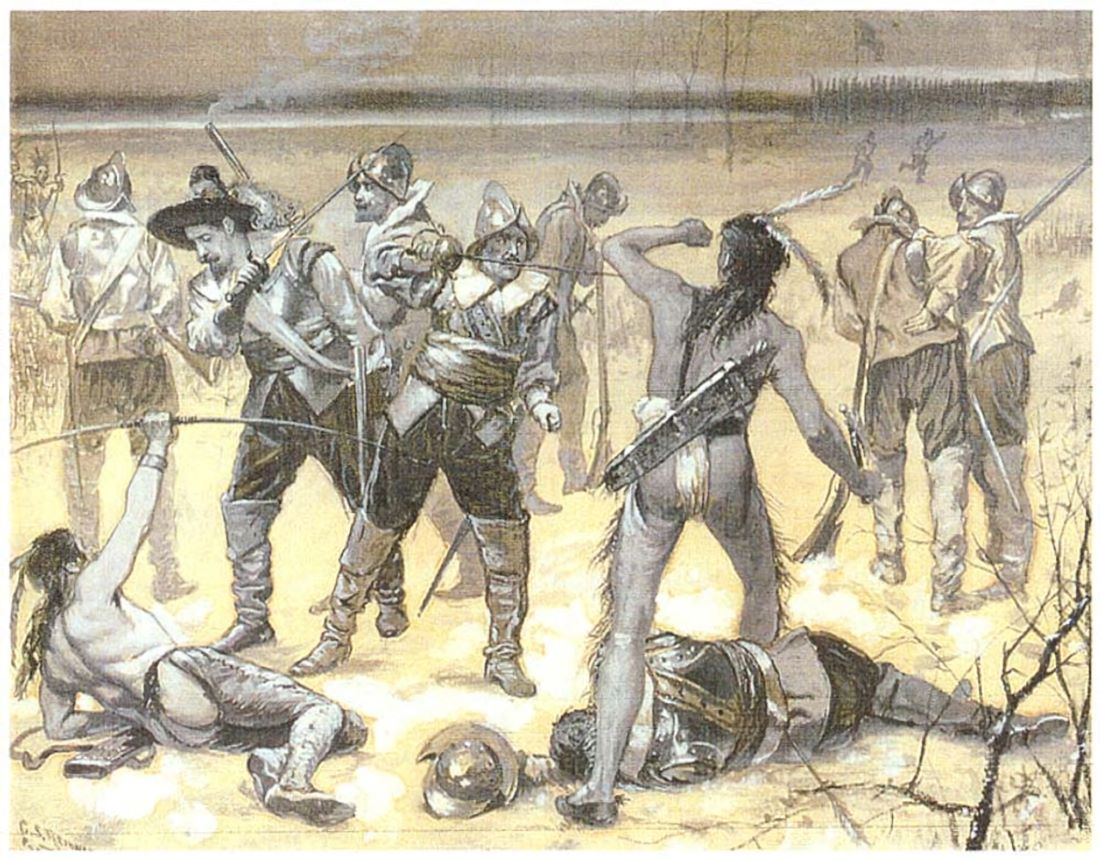

The war saw a coalition of English settlers from the Massachusetts Bay, Plymouth, and Connecticut colonies, along with their Native American allies, the Mohegan and Narragansett tribes, fighting against the Pequot. The conflict reached its peak with the Mystic Massacre in May 1637, where English forces and their allies attacked and burned a Pequot village, killing hundreds of men, women, and children. This brutal attack significantly weakened the Pequot’s ability to continue fighting and marked a turning point in the war.
Aftermath and Consequences
The aftermath of the Pequot War had profound and lasting effects on the Pequot people and the region. The Pequot were decimated, with estimates suggesting that between 500 to 700 were killed during the Mystic Massacre alone. Survivors were captured and sold into slavery or absorbed into other tribes, effectively dissolving the Pequot as a distinct entity. This marked the first significant instance of Native American displacement and subjugation by European settlers in New England.
The Pequot War set a precedent for future conflicts between Native American tribes and European settlers, illustrating the potential for violent and destructive encounters. It also demonstrated the colonists’ willingness to use extreme measures to secure their interests and expand their territories. The war’s outcome solidified the power of the English in the region and paved the way for further colonial expansion, often at the expense of indigenous populations. The Pequot War remains a pivotal event in American history, highlighting the complex and often tragic interactions between Native Americans and European settlers.
Historical Challenge: Can You Conquer the Past?
Answer more than 18 questions correctly, and you will win a copy of History Chronicles Magazine Vol 1! Take our interactive history quiz now and put your knowledge to the test!