How did Attila the Hun die has puzzled historians and scholars for centuries. Often termed the “Scourge of God,” Attila was a formidable leader, commanding the Hunnic Empire’s dominance over vast European territories during the 5th century. This legendary barbarian king, renowned for his fierce reputation, didn’t just intimidate the civilizations he met but also struck fear into the very heart of the mighty Roman Empire. However, despite the many tales of his epic conquests, the details of his sudden demise in 453 AD remain veiled in mystery. While there are several theories, a definitive cause of death continues to elude us.

Natural Causes:
According to the Roman historian Priscus, whose accounts serve as a primary source of information about Attila and the Huns, the king was found dead the morning after his wedding to the young Ildico. Priscus detailed a night of heavy feasting and drinking. From this, one prevailing theory posits that Attila may have suffered from a massive nosebleed due to a burst blood vessel, leading to him choking on his own blood. Another medical speculation aligns with the symptoms of esophageal varices — a condition where the veins in the esophagus can rupture due to chronic alcohol abuse. Historian Peter Heather, in his book “The Fall of the Roman Empire,” mentions that excessive drinking could have led to such an internal bleeding episode, especially if Attila had any underlying health issues.
Assassination:
Given Attila’s stature and the political intrigues of the time, theories of assassination naturally arise. Some narratives suggest that Ildico, his new wife, might have had a role in his death. However, this viewpoint largely stems from the simple fact that she was present during his last hours. Michael Babcock, in his book “The Night Attila Died,” brings forth the hypothesis that Attila was murdered, possibly with the complicity or direct involvement of the Roman Empire. The Romans, after all, had a significant stake in Attila’s demise given their tumultuous history.
External Conspiracy:
The Roman connection extends further into theories of an external conspiracy. Rome’s relief at the passing of such a formidable adversary cannot be understated. John Man’s “Attila: The Barbarian King Who Challenged Rome” delves into the possibility of a Roman-engineered assassination, emphasizing the tactical advantage Rome would gain from Attila’s removal. While tempting to consider, concrete evidence for this theory is scant.
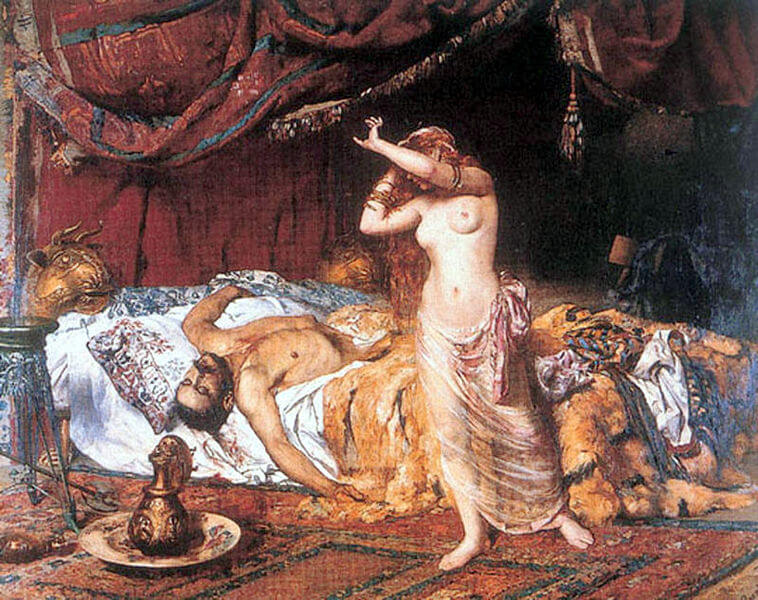
It is also crucial to highlight that the death of a leader like Attila, so central to his empire’s might, would inevitably spawn rumors and speculations. The political landscape of the era, rife with shifting alliances and betrayals, further complicates the matter. As historian David Nicolle noted in “Attila and the Nomad Hordes,” the Hunnic Empire’s enemies might have been eager to propagate notions of a dishonorable death, overshadowing his achievements.
In conclusion, the enigma of Attila the Hun’s death remains one of history’s intriguing puzzles. Despite the exhaustive investigations and numerous theories presented by historians and scholars, a definitive answer eludes us. It’s a testament to Attila’s enduring impact on history that, almost 1,500 years after his death, the circumstances of his demise continue to captivate and confound. While we may never know with absolute certainty how this mighty leader met his end, the legend of Attila, the ferocious Hunnic king who challenged empires, lives on.
Historical Challenge: Can You Conquer the Past?
Answer more than 18 questions correctly, and you will win a copy of History Chronicles Magazine Vol 1! Take our interactive history quiz now and put your knowledge to the test!

