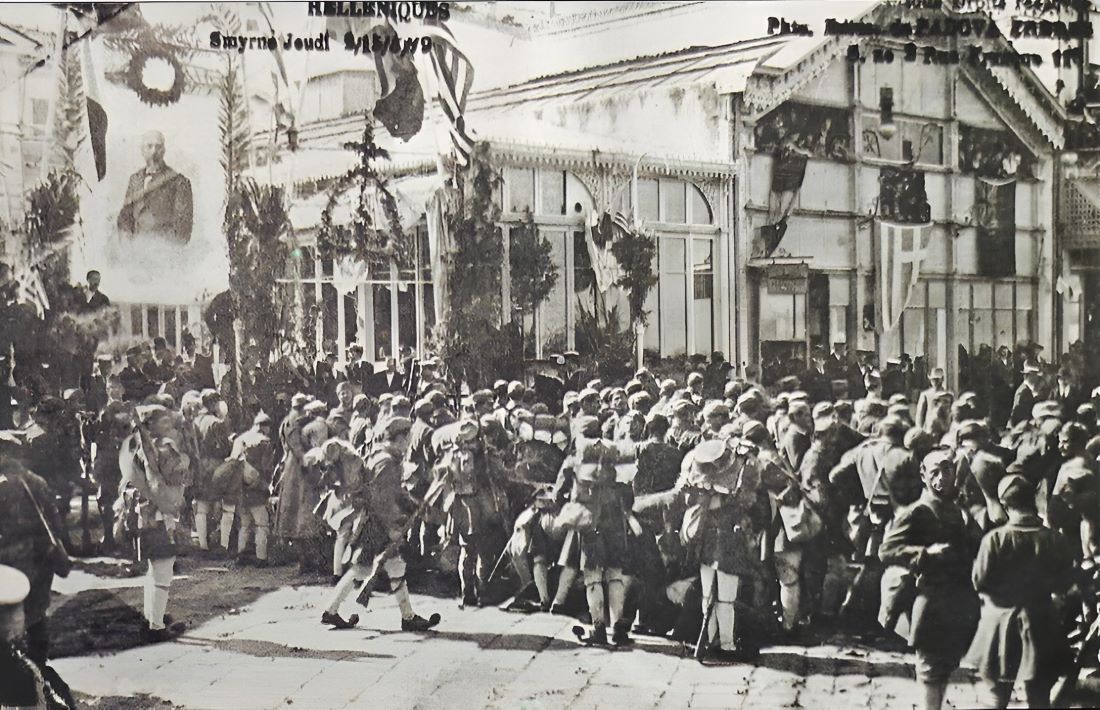
History has repeatedly shown that when one desires more than what is rightfully theirs, they risk losing even what they already possess. The Megali Idea, a grand vision of expanding Greek territory to encompass all regions inhabited by ethnic Greeks, is a prime example of such an ambition. Born out of nationalistic fervor in the 19th century, the idea sought to restore the glory of ancient Greece. However, its pursuit ultimately led to a devastating defeat in Asia Minor, forever altering the course of modern Greek history.
The Origins of the Megali Idea
The Megali Idea was conceived during the early 19th century, in the midst of Greece’s struggle for independence from the Ottoman Empire. Inspired by the rich heritage of classical Greece and Byzantine glory, many intellectuals and leaders sought to expand the newly-formed Greek state beyond its borders. They envisioned a greater Greece that would reclaim Constantinople, the Aegean islands, and parts of Asia Minor, uniting all Greek-speaking populations under one nation.
This vision was not merely an act of expansionism but was deeply rooted in a sense of historical justice. Greek leaders, such as Ioannis Kolettis, promoted the idea as a moral obligation to liberate fellow Greeks living under Ottoman rule. As he famously declared in 1844,
“The Kingdom of Greece is not the whole of Greece, it is only a part, the smallest and poorest part.”
Thus, the Megali Idea became intertwined with Greece’s national identity, growing stronger with each political victory.
The early successes of the Greek state, including the annexation of Thessaly and parts of Epirus, fueled further aspirations. However, the challenges were immense, as the Ottoman Empire still held significant Greek populations, and European powers had their own interests in the region. Nevertheless, the dream of a Greater Greece persisted, shaping foreign and domestic policies.
The Rise of Nationalism and Expansion
By the early 20th century, the Megali Idea had become the driving force behind Greece’s geopolitical ambitions. The Balkan Wars of 1912-1913 marked a significant step towards achieving the dream, as Greece successfully expanded its territory, gaining Thessaloniki and parts of Macedonia. These victories strengthened the national belief that the Megali Idea was not only possible but within reach.
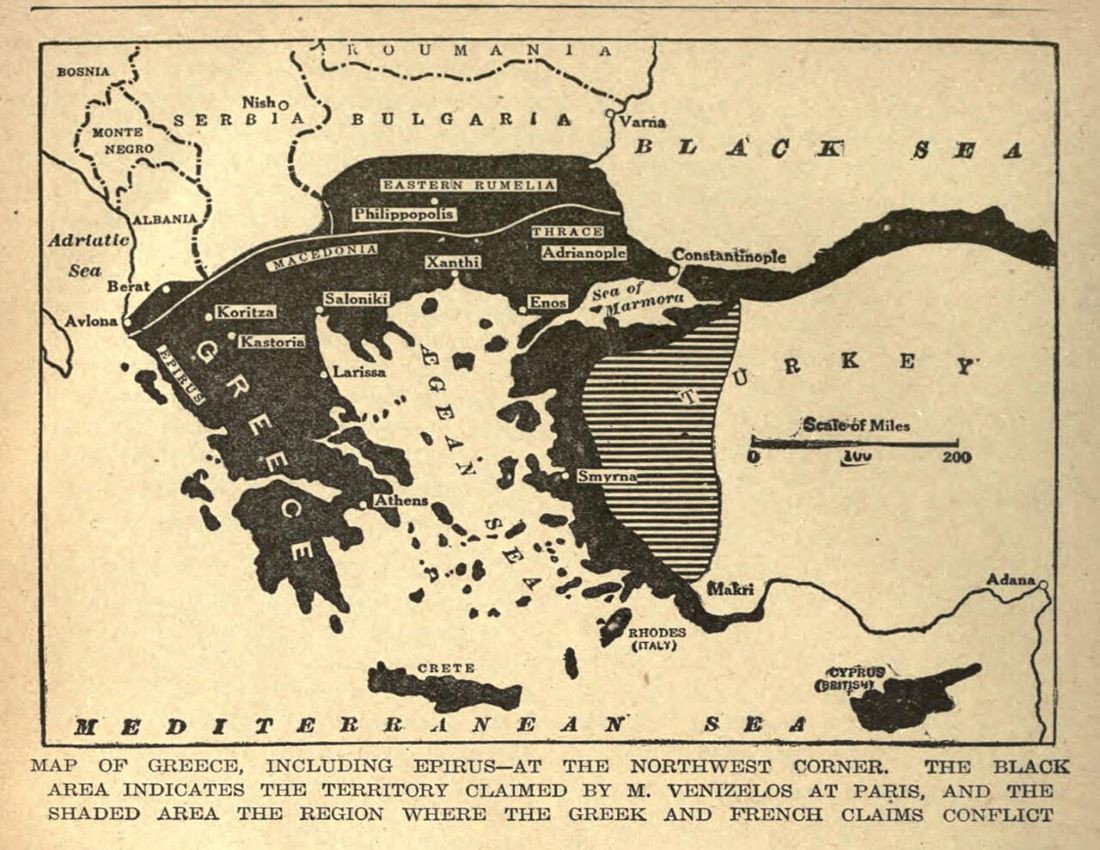
Greek Prime Minister Eleftherios Venizelos emerged as a champion of the cause. Under his leadership, Greece entered World War I on the side of the Allies, hoping to gain territorial concessions from a weakened Ottoman Empire. Venizelos’s vision was clear: a Greece that would stretch from the Aegean to the shores of Asia Minor, with Constantinople as its crowning jewel.
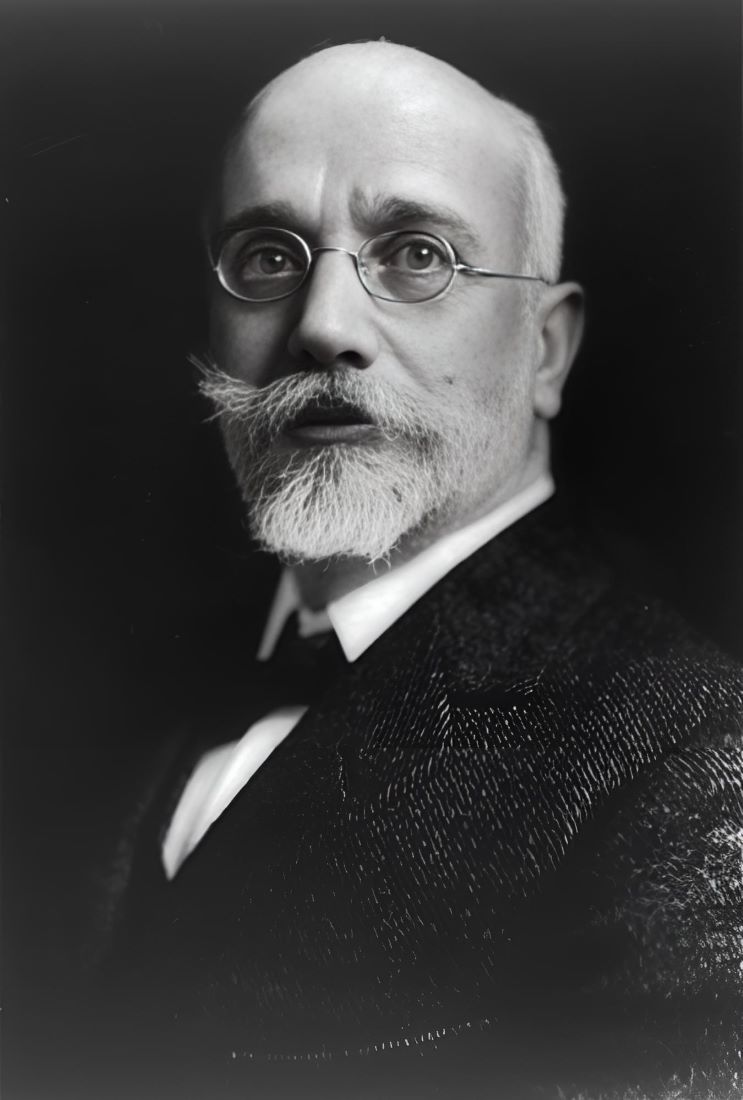

The Treaty of Sèvres in 1920 appeared to be the realization of this grand vision. The treaty granted Greece control over Smyrna (modern-day Izmir) and surrounding regions in Asia Minor, marking a high point in the pursuit of the Megali Idea. For a brief moment, it seemed that the dream of a Greater Greece was within reach.
The Asia Minor Catastrophe
Despite the initial success, the tide soon turned. The Greco-Turkish War of 1919-1922, ignited by Greek expansion into Asia Minor, became a pivotal moment in Greek history. Venizelos’s government believed that occupying Smyrna would lead to the eventual annexation of all Asia Minor territories inhabited by Greeks. However, the war quickly turned into a disaster.
Turkish forces, led by Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, mounted a fierce resistance. Greece’s military campaign, stretched too thin and lacking adequate resources, faltered. The Turkish nationalist movement grew stronger, and by 1922, the Greek army was in full retreat. The fall of Smyrna, with its destruction and the slaughter of Greek civilians, marked the catastrophic end of the Megali Idea.
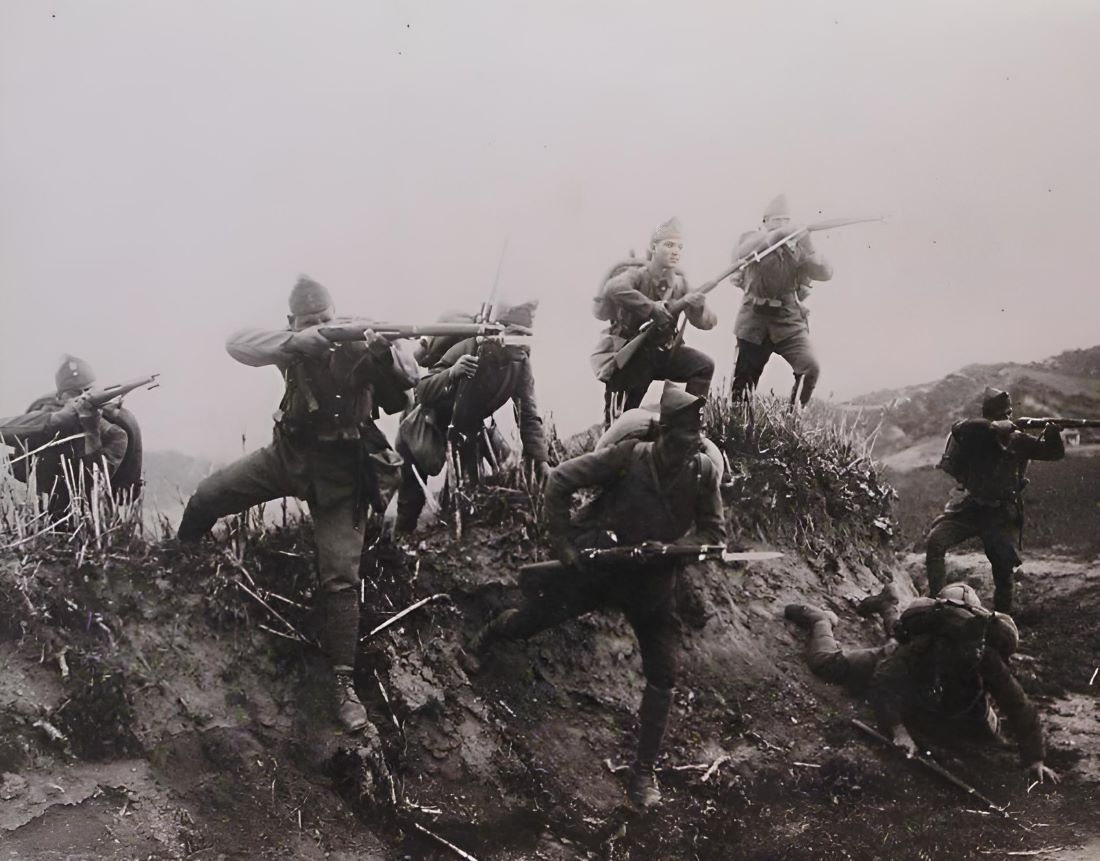

The defeat in Asia Minor not only crushed the dream of a Greater Greece but also led to one of the largest population exchanges in history. Over a million Greeks were forced to leave Asia Minor, their ancestral homeland for millennia. The Greco-Turkish War, thus, marked the final chapter of the Megali Idea, with Greece left to rebuild in the wake of immense human and territorial losses.
Legacy and Reflections
The fall of the Megali Idea left a profound mark on Greece. The national trauma of the Asia Minor Catastrophe shaped Greek identity for generations. The population exchange between Greece and Turkey solidified the boundaries between the two nations, and the vision of a Greater Greece was permanently abandoned. Many Greeks who had been displaced from their homes in Asia Minor brought with them their stories of loss and resilience, which became an integral part of modern Greek culture.
Indeed, the catastrophic end of this grand vision serves as a cautionary tale of the dangers of unchecked nationalism and the desire for territorial expansion. The Megali Idea, once a beacon of hope and national unity, became a symbol of hubris and tragic loss. It is a reminder that nations, in their quest for glory, must also reckon with the potential for devastating failure.
Historical Challenge: Can You Conquer the Past?
Answer more than 18 questions correctly, and you will win a copy of History Chronicles Magazine Vol 1! Take our interactive history quiz now and put your knowledge to the test!

